
#EXCESS ABDOMINAL FLUID TRIAL#
The American Liver Foundation receives contributions and funding from clinical trial and study sponsors but does not evaluate or endorse any clinical trials or studies, and is not affiliated with any of the sponsors.Discover information about different types of cancer Start your search here to find additional clinical trials that are looking for participants.

If someone continues to have fluid build-up or other treatments do not work, a doctor may consider a TIPS procedure ( transjuglar intrahepatic portosystemic shunt). The fluid will build back up and the procedure will need to be repeated. During paracentesis, a doctor, usually an interventional radiologist, uses ultrasound to guide a needle into the abdomen and drain the fluid out of the body. When this happens, someone may have a procedure called therapeutic paracentesis. Sometimes, diuretics are not enough, and the fluid will continue to build up.

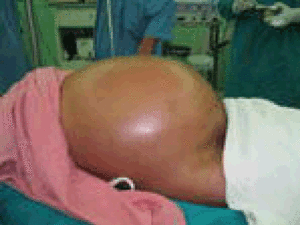
Medications called diuretics may be prescribed which make the kidneys excrete more sodium and water into your urine, causing you to pee more frequently. If you have ascites, be sure to learn more from a nutritionist who specializes in the liver about your unique needs. Reducing sodium, or salt, is a first line therapy for ascites. How is ascites treated?Īscites is treated with a low-sodium diet, medications called diuretics, removing the fluid, or surgery to reroute blood flow. Someone with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis will usually feel even more uncomfortable and experience tenderness in their abdomen and may develop a fever. This infection can also greatly impact the function of your kidney. If left untreated the infection can be fatal. Ascites can become infected for no reason which is called spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. This infection needs to be treated early with the right antibiotics. The belly becomes hard from the fluid buildup, may resemble a pregnancy belly and the belly button can become pushed out. Some people with ascites may develop swollen legs and ankles, called edema. When large amounts of fluid gather in the belly it can lead to swelling and pain and be very uncomfortable. People with liver disease may experience different amounts of fluid buildup – a little buildup of fluid may not cause any symptoms but as the amount of fluid increases it can cause waist size to expand and weight gain. The increased pressure of portal hypertension causes fluid to seep out and pool in the abdominal cavity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
